When it comes to deciphering the intricate world of financial analysis, understanding how to feed data from financial statements into a fair value calculator can be your golden ticket to making informed investment decisions. Imagine standing at the helm of your financial future, equipped with the tools to unlock the true potential of your investments. This is not just about crunching numbers, it’s about transforming raw data into meaningful insights that guide you toward rewarding opportunities. In this blog post, we will unravel the complexities and empower you with the knowledge to translate financial statements into actionable data.
The process might seem daunting at first glance, yet the benefits are undeniable. Consider this: according to recent surveys, investors who diligently incorporate fair value calculations into their strategy outperform those who rely solely on market trends by a significant margin. The ability to accurately assess an asset’s worth can mean the difference between seizing a lucrative opportunity or overlooking a hidden gem. By comprehending the nuances of financial statements and mastering the art of data feeding, you’ll position yourself strategically in an ever-competitive market landscape. Get ready to elevate your financial acumen and navigate the investment world with confidence.

Understanding the Role of Financial Statements in Investment Analysis
Financial statements serve as the foundation for any rigorous investment analysis. They provide a snapshot of a company’s financial health, profitability, and risk exposure. When pondering how to feed data (from financial statements) into a fair value calculator? the first step is appreciating why these documents matter. Investors rely on the balance sheet, income statement, and cash flow statement to gauge solvency, operational efficiency, and liquidity.
Each statement plays a distinct role: the balance sheet reveals assets versus liabilities, the income statement tracks revenues and expenses over a period, and the cash flow statement shows real cash movements. Together, they present a holistic view of corporate performance. By interpreting these figures correctly, analysts can discern trends such as revenue growth or debt accumulation, key factors that influence fair value outcomes.
Understanding these roles not only sharpens your analytical lens but also ensures that the data you feed into your fair value calculator is relevant and robust. Accuracy at this stage prevents skewed valuations and misleading conclusions. Ultimately, grasping the role of financial statements equips you to transform raw accounting figures into strategic insights that inform better investment decisions.
Introduction to Fair Value Calculation
Fair value calculation is a methodology used to estimate the intrinsic worth of an asset or a company. Unlike market price, which fluctuates with supply and demand, fair value reflects a reasoned estimate based on underlying fundamentals. Mastering how to feed data (from financial statements) into a fair value calculator? begins with selecting an appropriate valuation model, such as discounted cash flow (DCF), dividend discount model (DDM), or comparables analysis.
In a DCF model, for instance, you project future cash flows and discount them back to present value using a suitable discount rate. This rate often reflects the company’s weighted average cost of capital (WACC). On the other hand, comparables analysis involves benchmarking multiples like P/E or EV/EBITDA against peers to derive a relative fair value. Each model demands specific inputs from financial statements, reinforcing the importance of precise data gathering.
Adopting a systematic approach to fair value calculation minimizes biases and improves consistency. By understanding the mechanics behind your chosen model and the quality of data inputs, you’ll produce valuations that are credible and defendable. This practice not only enhances your confidence in investment theses but also positions you to identify undervalued or overvalued opportunities more effectively.
Key Components of Financial Statements for Data Feeding
When it comes to feeding your fair value calculator, not all line items hold equal weight. Focus on components that directly impact valuation models, assets, liabilities, revenue streams, costs, and cash flows. Identifying these key elements simplifies the data extraction process and reduces the risk of overloading your model with irrelevant figures.
Prioritize balance sheet totals like current assets, long‐term debt, and shareholder equity. From the income statement, emphasize net revenue, operating expenses, and net income. On the cash flow statement, track operating cash flows and capital expenditures. Once you’ve pinpointed these components, ensure they’re formatted consistently, this consistency streamlines the integration of data into your chosen valuation framework.
By zeroing in on these critical components, you’ll enhance the accuracy of your fair value calculations and avoid common pitfalls such as double counting or using outdated figures. Accurate data feeding hinges on clarity: understanding which metrics matter most and why.
Explore our most popular stock fair value calculators to find opportunities where the market price is lower than the true value.
- Peter Lynch Fair Value – Combines growth with valuation using the PEG ratio. A favorite among growth investors.
- Buffett Intrinsic Value Calculator – Based on Warren Buffett’s long-term DCF approach to determine business value.
- Buffett Fair Value Model – Simplified version of his logic with margin of safety baked in.
- Graham & Dodd Fair Value – Uses conservative earnings-based valuation from classic value investing theory.
- Intrinsic vs. Extrinsic Value – Learn the core difference between what a company’s really worth and what others pay.
- Intrinsic Value Calculator – A general tool to estimate the true value of a stock, based on earnings potential.
- Fama-French Model – For advanced users: Quantifies expected return using size, value and market risk.
- Discount Rate Calculator – Helps estimate the proper rate to use in any DCF-based valuation model.
Best Practices for Extracting Data from Balance Sheets
Extracting data from balance sheets demands a systematic approach to guarantee accuracy. Start by verifying the reporting period and currency to ensure consistency with other financial statements. Convert foreign currency figures if necessary and adjust for any quarterly snapshots when building an annual model.
Next, reconcile the totals for assets, liabilities, and equity. Confirm that assets equal the sum of liabilities plus equity; any discrepancy suggests an accounting error or incomplete data. Pay particular attention to non‐current assets such as intangible assets or goodwill, these items often require adjustments for impairment or amortization when inputting into your fair value calculator.
Finally, document any restatements or adjustments made during the extraction process. Keeping a clear audit trail not only helps when updating the model but also strengthens the transparency and credibility of your valuation exercise.
Leveraging Income Statements for Accurate Data Input
The income statement delivers a chronological view of revenues and expenses, offering insights into profitability and operational efficiency. When feeding data into your fair value calculator, begin by isolating net sales or revenue. This top‐line figure forms the basis for projecting future earnings and cash flows.
Next, break down operating expenses into categories such as cost of goods sold (COGS), selling, general, and administrative expenses (SG&A), and depreciation. Understanding these cost drivers informs margin analysis and growth assumptions. Don’t overlook extraordinary items or one‐time charges; adjusting these figures ensures your model reflects sustainable earnings potential.
Finally, calculate earnings before interest and taxes (EBIT) and net income. These metrics often feed directly into valuation multiples or serve as inputs for cash flow projections. Accurate extraction and adjustment of income statement data prevent over-optimistic growth assumptions and lead to more trustworthy fair value outputs.
💡 Discover Powerful Investing Tools
Stop guessing – start investing with confidence. Our Fair Value Stock Calculators help you uncover hidden value in stocks using time-tested methods like Discounted Cash Flow (DCF), Benjamin Graham’s valuation principles, Peter Lynch’s PEG ratio, and our own AI-powered Super Fair Value formula. Designed for clarity, speed, and precision, these tools turn complex valuation models into simple, actionable insights – even for beginners.
Learn More About the Tools →Utilizing Cash Flow Statements in Fair Value Calculations
Cash flow statements are critical for any DCF-based valuation model. They reveal the true cash generated by a business, stripped of non‐cash accounting entries. To feed your fair value calculator, start by extracting operating cash flows, which represent the cash generated by core operations.
Next, identify capital expenditures (CapEx) under investing activities. Subtract CapEx from operating cash flows to arrive at free cash flow (FCF), the primary input for discounted cash flow analyses. Remember to adjust for changes in working capital—positive increases signal cash tied up in receivables and inventory, while decreases release cash back into the business.
Lastly, consider any financing cash flows related to debt issuance or repayments, though these are typically excluded from FCF calculations. By focusing on operating cash flows and CapEx, you’ll provide your fair value calculator with the cleanest, most relevant data for projecting future cash flows and estimating intrinsic value.
Importance of Consistency and Accuracy in Data Entry
Consistency in data entry is paramount when building or updating a fair value calculator. Variations in reporting periods, currencies, or accounting standards can introduce significant errors. Always standardize your data set before feeding figures into the model to maintain comparability across time and entities.
Accuracy goes hand in hand with consistency. Manual data entry is prone to typographical mistakes, which can drastically alter valuation results. Employ validation checks, such as reconciling subtotals and comparing inputs against original financial statements, to catch errors early. Automating parts of the data extraction and entry process can further reduce the risk of human error, ensuring that your fair value outputs remain robust and defendable.
By emphasizing both consistency and accuracy, you’ll reinforce the integrity of your valuation models. Reliable data inputs lead to credible fair value estimates, empowering you to make well-founded investment decisions.
Tips for Efficient Data Feeding Processes
Speed and precision are essential when working through large volumes of financial data. Begin by creating a standardized template for data entry, with clearly labeled fields for each required metric. This template ensures that every new data set aligns seamlessly with your fair value calculator’s structure.
Leverage modern tools such as OCR (optical character recognition) software or specialized financial data extraction services. These technologies can auto-read PDFs and financial reports, populating your template with minimal manual intervention. Always conduct spot checks on automatically extracted data to confirm accuracy.
Develop a version control system to track changes across different iterations of your model. This practice not only aids collaboration among team members but also allows you to revert to prior versions if a data discrepancy emerges. Through these strategies, you’ll optimize your workflow and maintain high standards of data integrity.
Enhancing Investment Decision-Making with Fair Value Calculations
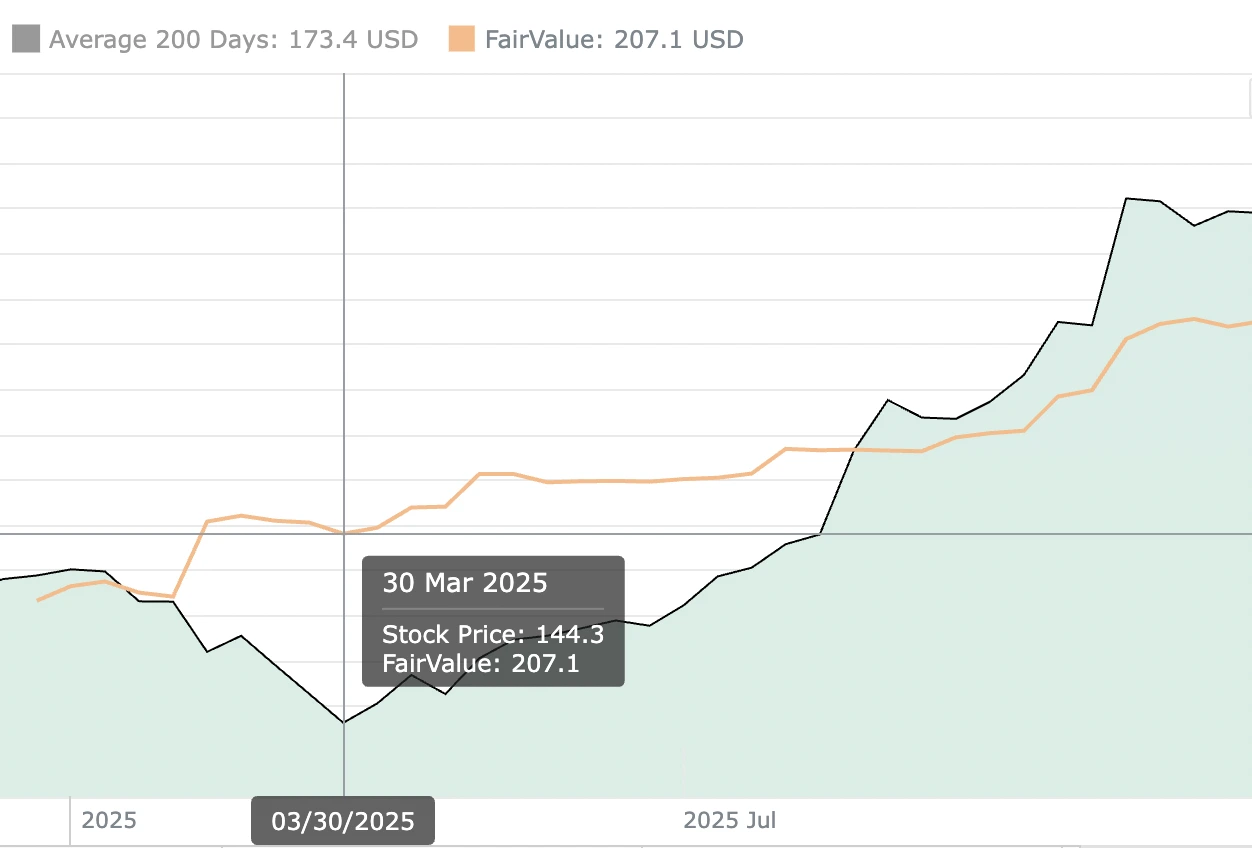
Incorporating fair value calculations into your investment process transforms raw financial data into actionable intelligence. By understanding how to feed data (from financial statements) into a fair value calculator? you gain clarity on whether a security is undervalued, fairly priced, or overvalued compared to its intrinsic worth.
Armed with these insights, you can craft investment strategies that capitalize on market inefficiencies. For instance, if your analysis reveals a stock trading below its calculated fair value, it may warrant a buy recommendation. Conversely, identifying overvalued assets could prompt timely profit-taking or risk mitigation measures.
Ultimately, a rigorous fair value approach equips you with a competitive edge. It fosters discipline, reduces emotional decision-making, and provides a quantitative basis for portfolio adjustments. Whether you’re a seasoned professional or a retail investor, mastering this process enhances your ability to navigate volatile markets and seize high-probability opportunities.
Conclusion: Empowering Your Investment Journey
Mastering how to feed data from financial statements into a fair value calculator is more than a technical exercise, it’s a strategic capability that underpins sound investment decisions. By systematically extracting, validating, and integrating key financial metrics, you’ll generate valuations that stand up to scrutiny and guide your portfolio choices.
Embrace these practices to elevate your analytical rigor and unlock new levels of confidence in your investment journey. With accurate data feeding and robust fair value insights at your fingertips, you’re well-positioned to identify opportunities and manage risks in any market environment.